Before you leave...
Get 10% off your first order
10% off
Enter the code below at checkout to get 10% off your first order
Couldn't load pickup availability
One day shipping within Chennai.
2-3 days shipping across India.
Safe and trusted for kids.
Trusted quality for every child.
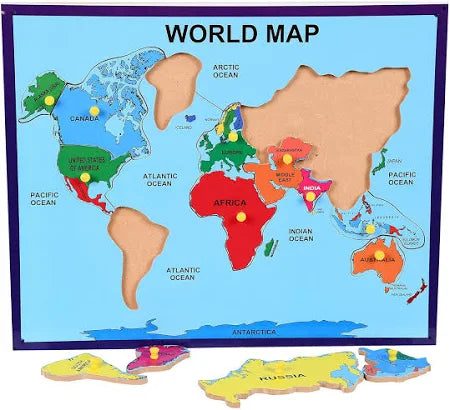
A world map is a visual representation of Earth’s entire surface, showing the continents, oceans, and countries in their relative positions. Because the Earth is a sphere and a map is flat, world maps always involve some distortion in shape, area, distance, or direction, depending on the map projection used.
Here’s a detailed description:
Continents:
Asia – The largest continent, occupying the eastern and northern hemispheres; includes countries like China, India, and Russia.
Africa – South of Europe and bordered by the Atlantic and Indian Oceans; notable for its large landmass and diverse geography.
North America – Lies entirely in the Northern and Western Hemispheres; includes the U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
South America – Extends mostly in the Southern Hemisphere; home to the Amazon rainforest and Andes Mountains.
Europe – West of Asia and north of Africa; smaller but densely populated.
Australia (Oceania) – The smallest continent, including Australia, New Zealand, and Pacific islands.
Antarctica – The southernmost continent, covered almost entirely in ice.
Oceans:
Pacific Ocean – The largest and deepest, between Asia/Australia and the Americas.
Atlantic Ocean – Between the Americas and Europe/Africa.
Indian Ocean – Between Africa, Asia, and Australia.
Southern Ocean – Surrounds Antarctica.
Arctic Ocean – Around the North Pole.
Lines and Coordinates:
Equator (0° latitude): Divides the Earth into Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Prime Meridian (0° longitude): Passes through Greenwich, England; divides Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Tropics: Tropic of Cancer (north) and Tropic of Capricorn (south) mark the limits of the tropics.
Polar Circles: Arctic and Antarctic Circles mark the cold regions near the poles.
Projections (Map Types):
Mercator Projection: Preserves shape but distorts size near poles (Greenland looks huge).
Robinson Projection: Balances shape and size—often used in classrooms.
Peters Projection: Keeps area accurate but distorts shapes.
Other Features:
Political boundaries (countries, capitals)
Physical features (mountain ranges, rivers, deserts)
Latitude/longitude grid
Scale and compass rose for orientation
Thanks for subscribing!
This email has been registered!
Get 10% off your first order
Enter the code below at checkout to get 10% off your first order